In this issue:
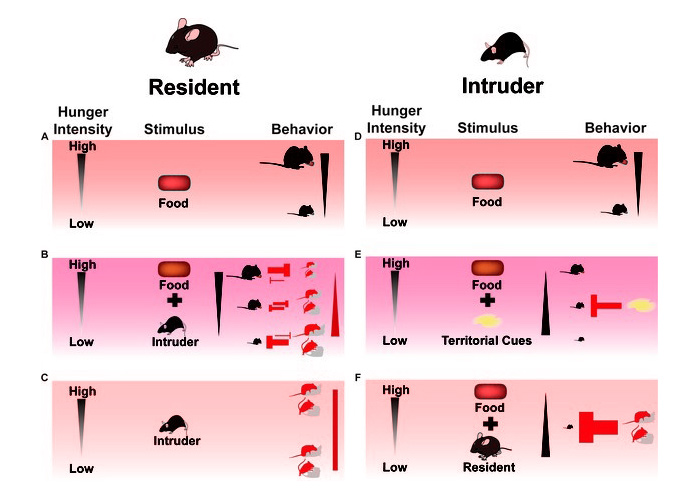
When presented with a choice, organisms need to assimilate internal information with external stimuli and past experiences to rapidly and flexibly optimize decisions on a moment-to-moment basis. The team hypothesized that increasing hunger intensity would curb expression of social behaviors such as mating or territorial aggression; the team further hypothesized social interactions, reciprocally, would influence food consumption. The team assessed competition between these motivations from both perspectives of mice within a resident-intruder paradigm. The team found that as hunger state escalated, resident animal social interactions with either a female or male intruder decreased. Furthermore, intense hunger states, especially those evoked via AgRP photoactivation, fundamentally altered sequences of behavioral choice; effects dependent on food availability. Additionally, female, but not male, intrusion attenuated resident mouse feeding. Lastly, the team noted environmental context-dependent gating of food intake in intruding mice, suggesting a dynamic influence of context cues on the expression of feeding behaviors.
Materials and methods: Photostimulation protocol
Fiber optic cables were firmly attached to the implanted fiber optic cannulae with zirconia sleeves and coupled to lasers via a fiber-optic rotary joint. During photostimulation experiments, light pulse trains were programmed using a waveform generator that provided input to a blue light laser (473 nm; Laserglow). The team adjusted the light power of the laser such that the light power exiting the fiber optic cable was 10–12 mW using an online light transmission calculator for brain tissue. The team estimated the light power at the ARC at 4.99 mW/mm2. Note that this is likely a high estimation because some light was probably lost at the interface between the fiber optic cable and the implanted fiber optic cannula.
Discussion
Overall, the team has demonstrated more dynamic interaction between two mutually exclusive motivations – hunger and social interaction – than has previously been appreciated in recent neuroscience research. The team has shown that in rodents, the context of a social interaction, including territorial ownership and hunger state, can prominently guide how behavioral encounters will unfold. Subsequent research should further address the neurophysiology of homeostatic feeding circuitry both upstream and downstream of ARCAgRP neurons that may principally alter the interplay of these two orthogonal motivations and their behavioral expression in real time. Furthermore, future high-level modeling of decision-making will advance the field’s understanding of computational choice behavior.
Full access to the materials and methodology, can be found by clicking here.
Details on the 473 nm laser used in the research can be found by clicking here.

